top of page
VB.Net
What is it?
-
ASP.NET is an open source web application framework created by Microsoft.
-
It allows programmers to develop dynamic websites and web services.
-
It provides integration of HTML, CSS and JavaScript.
History
-
First released in January 2002.
-
Developed by Microsoft.
-
Successor of Active Server Page (ASP)
Configure VB.Net
Environment Setup
-
First released in January 2002.
-
Developed by Microsoft.
-
Successor of Active Server Page (ASP)

The Hello World
-
First released in January 2002.
-
Developed by Microsoft.
-
Successor of Active Server Page (ASP)


Basics of VB
-
VB.Net is an object-oriented programming language.
-
Class
-
Instance
-
Methode
-
Instance Variable
Class
-
Class is a Blueprint of object.
-
Class means, it can have logic, which can be instantiated.
-
All the methods & variables inside a class are members.
-
We declare class with keyword Class ClassName, then members & and ends with End Class.


Constructors & Destructors
Constructor
-
It is a sub, Declared as Sub New( ), then statement & End Sub.
-
Executed when an object is created.
-
It can have a parameter passed while instantiation.
Destructor
-
It is a sub, executed when the object of a class goes out of scope.
-
Declared as Sub Finalize( ), then statement & End Sub.
-
It can't contain parameters, executed at last.


Methods
-
Shared methods or static methods can be invoked without creating an object of the class.
-
Instance methods are invoked through an object of the class
-
Sub Main ( ) is the Entry of a Program.
-
Declaring inside Class, Public Shared Sub Main( )
-
Declaring inside Module, Public Sub Main( )
Identifiers
-
The identifier is a name used to name a Class, Module, Function, Variable etc.
-
Here is some rules:
-
It must starts with leter
-
Can contin numbers (0 - 9)
-
Can have (_)
-
Can not have these characters : ? - +! @ # % ^ & * ( ) [ ] { } . ; : " ' / and \
-
Should not be Reserved Keyword
-
Datatypes
-
Data types refer to an extensive system used for declaring variables or functions of different types.
-
VB have wide range of Datatypes:
-
Boolean
-
Byte
-
Char
-
Date
-
Decimal
-
Double
-
Integer
-
Long
-
Object
-
SByte
-
Short
-
Single
-
String
-
UInteger
-
ULong
-
UShort
-
User-Defined datatype
-


Type Conversion Function
-
There are some predefined functions for converting one datatype to another datatype.
-
Here are some example out of 16 conversion function.:
-
CInt (expression) - Convert to Integer datatype
-
Clng (expression) - Convert to long datatype
-
CUShort(expression)
-
CBool(expression)
-
CBool(expression)
-
CObj(expression)
-
etc
-
Variable
-
A variable is nothing but a name given to a storage area that our programs can manipulate.
-
The Dim statement is used to declare a variable.
Access Modifier
-
Access modifiers decide accessibility of your class or class member.
-
There are 5 access modifier in VB.Net
Access modifier
Public
Private
-
Applicable only to the members of a type.
-
Accessible inside the class.
-
Classes and class members marked with Public
Protected
-
Private but can be inherited.
-
Applicable to class and members.
Friend
-
Available only inside the project.
-
Applicable to class and members.
Protected friend
-
Access to the same project.
-
And can be inherited
Accepting Value from User
-
The Console class in System namespace provides a function ReadLine for accepting input from user.
-
Here is a program asking Name and Age, and prints out a sentence.


Compiling .vb file
Executing .exe file
Asks user input & Prints a sentence.
Constant in VB
-
Constant refers to a fixed value in a program which can not be altered.
-
With Const keyword, we can declare the constant value.
-
Here are some constant value for printing & display in Visual Basic.

-
Enum
-
An enumeration type is declared by Enum statement.
-
It is a an Integer type by default.
-
We can change using As Datatype while declaring.
-
The defined value can be used at Class, Module, Structure, procedure or block level.
Compiler Directives
-
These directives give instructions to compiler to preprocess the information before actual Compilation starts.
-
Follwoings are some directives:
-
#Const Directives
-
#ExterialSource Directive
-
#IF... THAN... #ELSE Directives
-
#Region Directive
-
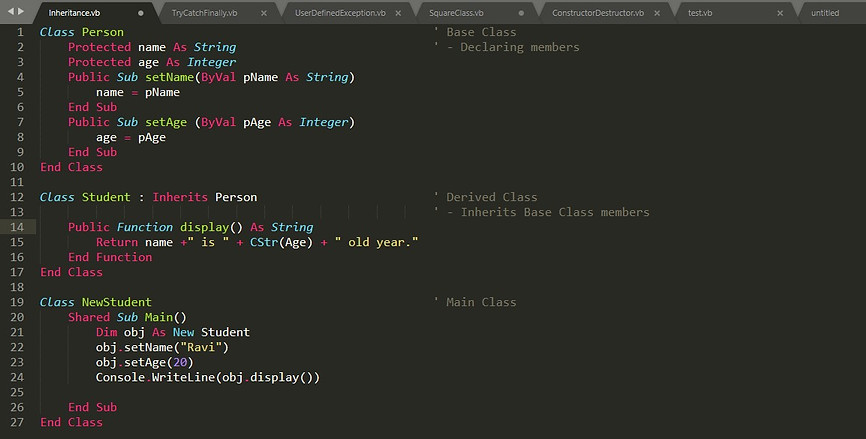
Inheritance
-
All the properties & methods of a Class/Interface can be reused by a Class
-
Parent class is called Base Class, where members are declared.
-
Child class is called Derived Class, where we can access those members.
-
Syntax of declaring Derived Class: Class cName : Inherits BaseClassName
-
Protected DIm a
-
Protected Dim b
-
Public Sub Abc()
Base Class
: Inherits
-
Uses those Members fof Base Class
-
Can overide Sub
-
Can have more Mebers
Derived Class

Conditional Statement:
-
These are the decision-making statements on the conditions.
-
Here are 3 conditonal statements:
-
IF ELSE
-
SELECT CASE
-
Nested IF, Select
-

Conditional Loops:
Do Loop
-
Do While (condition)... Loop
-
Do... Loop While (condition)
-
Do Until (condition)... Loop
-
Do... Loop Until (condition) Loop


While
-
Here the block code executed while the condition is TRUE.
-
Syntax: While condition ... End While
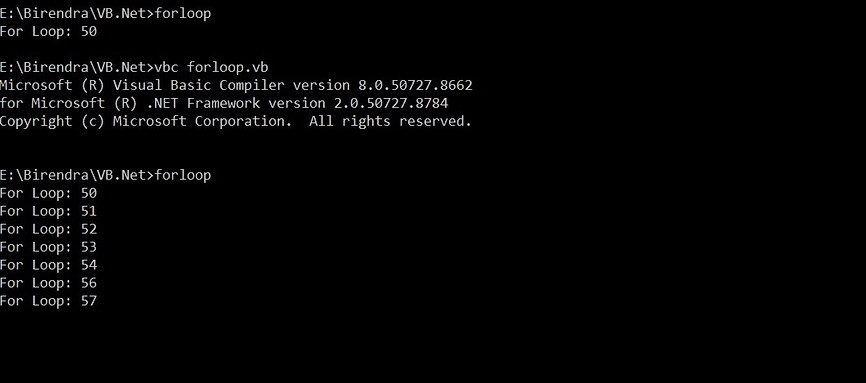
For Next
-
It iterates the code for a specified number of times.

For Each
-
For an iteration of Array or Collection elements we use For Each loop.E
-
Syntax: For Each elementVar In arrayName ... Next


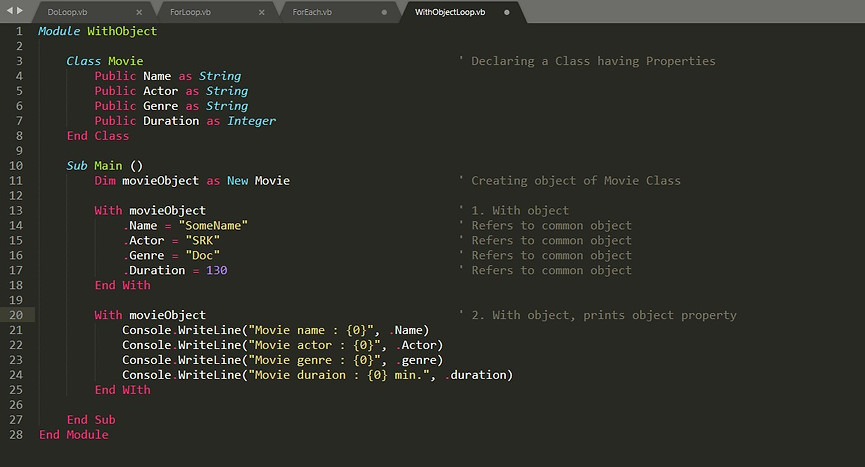
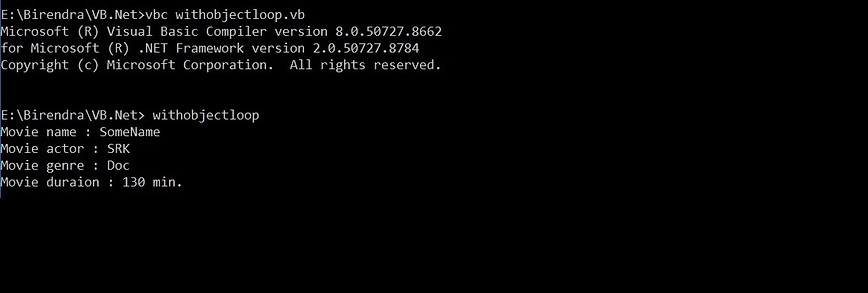
With Object
-
It is not a loop.
-
It executes a block of statements that refer to a common object/reference.
-
Syntax: With obj ... End With
Loop Control Statement
-
It changes the execution from a loop.
-
Here are 3 conditional statements:
-
Exit for/ while: Terminates the loop
-
Continue for/while: Skip the remainder of the body, continue to re-iterate.
-
GoTo line1: Transfers control the labeled statement.
-
Collection
-
Collection stores a wide range of data.
-
Unlike Array, it can store different datatypes.
-
Memory size allocates as it contains elements.
Types of Collection
-
All classes are belongs to System.Collections namespace.
-
Here are some collection classes.
System.Collection
ArrayList
HashTable
Queue
Stack
ArrayList
-
Stores index bases elements.
-
Unsorted elements access.

HashTable
-
It contains Key & value pair.
-
We can access keys & values.
-
It order to access keys, it needs to call ht.Keys which is ICollection class type.


Queue
-
Stores one value.
-
The first entered elements is being accessed in first. (FIFO)


Stack
-
Here we access the element in Last in First Out (LIFO) order.
-
It stores the elements like Stacks do; one after a


String
-
An array of characters.
-
An object of Stystem.String class.
-
Can declare as String.
Creation of String
-
A string can be created by following ways:
By String literal
Dim var as String = "Stone"
Using String Class Constructor
var = new String (charArray)
Ways of
creating String:
Property of Method returns String datatype
var = String.Join(" , ", stringArray)
By formatting method, which converts object to String type
var = String.Format("{0:t}", dateTime)
-
The below program shows Declaring and Creating String.


String Methods:
-
String class has some Properties & methods given below for string manipulation.
-
Here is 2 properties of String class:
-
string1.Chars( 2 ): Returns char at a specified index.
-
string1.Length( ): Gets the length of a string.
-
-
Below table has some static and non-static String method with description:
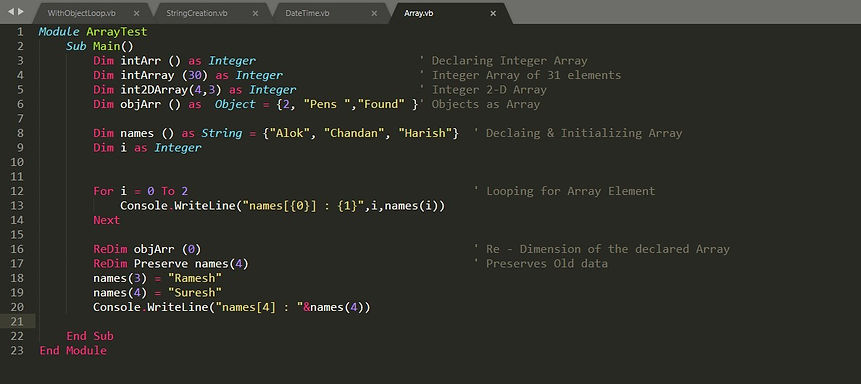
Array:
-
Is used to store a collection of data of the same datatype.
-
We can store/access from an index of a collection.
-
We declare an array by variable followed by ( ) or (size).

-
Array Class is defined on System namespace.
-
It has some properties & methods for manipulating the array object.
Array Properties:
-
arr1. IsReadOnly : Returns True if Read only
-
arr1. Length : Returns array length
-
arr1. Rank : Returns which dimension
Array Methods:
-
Array class has some static and non-static methods handle the array.
-
Static methods can be called by Array. and method name.
-
A non-static method can be called by arrayObject. and method name.
Collection:
-
Is used to store a collection of data of the same datatype.
-
We can store/access from an index of a collection.
-
We declare an array by variable followed by ( ) or (size).
Programs
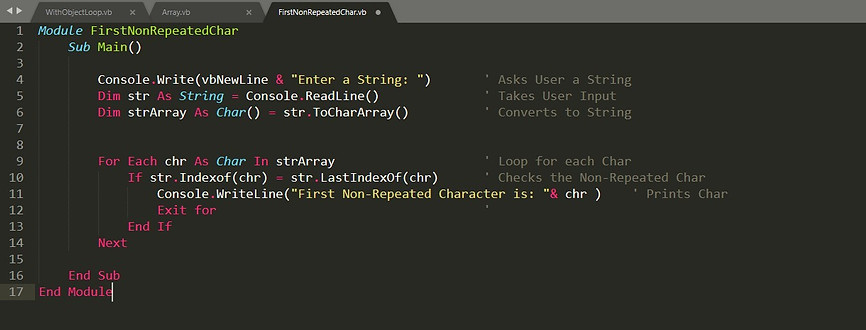
Program 1
-
Find the First non-repeated characher in a String.
-
Input: stoneprofits
-
Output: n

Program 2
-
Find Permutation of a Sting.
-
Input: ab
-
Output: ab, ab


Program 3
-
Find Digit Identification if string have any number.
-
Input: stone123profits
-
Output: TRUE, it contains number.

-
We checked here, with 2 string; one with number and another without number.
-
Here is the result shown in command prompt.

Program 4
-
Find & Replace the 1st highest repeated character with user given value.
-
Input: abcabab
-
Output: pbcpbpb
-
The output on Command Prompt looks like below.
Program 5
-
WAP to print a Numbered Diamond.
-
Input: 5
-
Output: -

-
The Diamond output is here.
-
It asks a number as user input for make a diamond.

Program 6
-
WAP to sum the numbers in a String.
-
Input: stone123profits7
-
Output: 130
File Handle in VB
-
File is a collection of data stored in disk.
-
In VB.Net we can pass the data through a communication path called stream.
-
There are lot of classes in System.IO availble for accessing Files.
Read File
-
There is StreamReader class is used to read text files.
-
This class inherits TextReader & Stream abstract classes.

Write File
-
We used StreamWriter class for writting a text file.
-
A array of strings is created, then we inserted data to file object with a string array loop.

Exception Handling
-
An exception is an unwanted error which breaks the execution flow of a program.
-
To continue the flow of execution, we can keep the codes in a block is called Exception Handling.
-
Here we can transfer the control from one part of a program to another, using this keyword:
-
Try: Where exception raised.
-
Catch: If exception, exceptions are being handled here.Can have multiple catches.
-
Finally: Inside this block, codes are executed regardless of exception is raised.
-
Throw: A program throws an exception.
-
Exception Classes
-
VB.Net is an object-oriented programming language.
Hierarchy of Exception Classes
System.Exception
System.ApplicationException
ArithmeticException (DevidedByZeroException)
IndexOutOfBoundException
ArgumentException (ArgumentOutOfBoundException)
System.SystemException
(User-Defined Exception Classes)
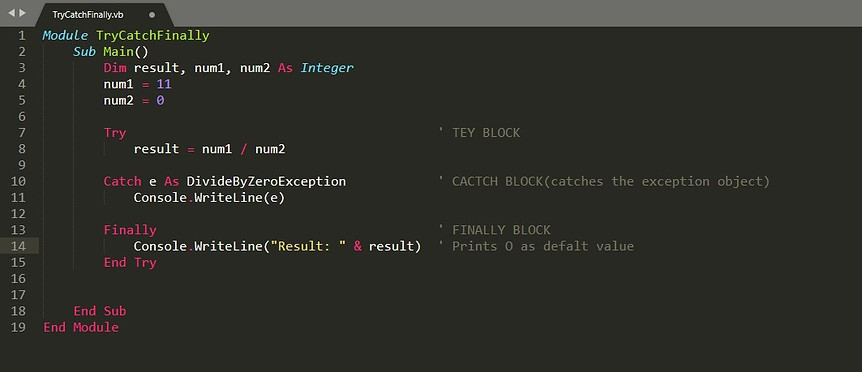
User-Defined Exception
-
In VB.Net, user can create an Costumized-Exception class, and thow this object.
-
To do so, the User-Defined Exception class must inherits ApplicationException class.
-
Here we called Base-Class constructor with message as string.
-
Thow the user object inside a condition using throw keyword.


VB.Net & Database
-
An exception is an unwanted error which breaks the execution flow of a program.
-
To continue the flow of execution, we can keep the codes in a block is called Exception Handling.
-
Here we can transfer the control from one part of a program to another, using this keyword:
-
Try: Where exception raised.
-
Catch: If exception, exceptions are being handled here.Can have multiple catches.
-
Finally: Inside this block, codes are executed regardless of exception is raised.
-
Throw: A program throws an exception.
-
Connect with SQL Server
Step 1
-
Create a Connection object.
Step 2
-
Use SqlConnection object to open the connection.
Step 3
-
Create a command object.
Step 4
-
Create a SqlDataReader object to Retrieve the data from SQL server.
-
Execute the query & store the result in DataReader.
Step 5
-
Loop over the DataReader and display the data.



Database
Command Line
bottom of page