top of page
JavaScript
What is it?
-
JavaScript is an object-based scripting language that is lightweight and cross-platform.
-
JavaScript is not compiled but translated. The JavaScript Translator (embedded in the browser) is responsible to translate the JavaScript code.
-
It is designed for creating network-centric applications.
-
Web pages are not the only place where JavaScript is used. Many desktop and server programs use JavaScript.
Use of JavaScript
-
JavaScript is used to create interactive websites.
-
It is mainly used for:
-
Client-side validation
-
Dynamic drop-down menus
-
Displaying data and time
-
Displaying clocks, graphs etc.
-
Displaying pop-up windows and dialog boxes.
How it works?
-
The browser has 3 main programs installed in.
A Browser has 3 major components installed.

DOM Parser
For HTML code.
CSS Parser
For CSS code.
JavaScript Engine
To process JavaScript code.
-
JavaScript code is processed by a JavaScript Engine on a browser.
-
The different browser has different JavaScript compiler installed.
-
Below table shows the JS engine of the popular browsers.
JIT (Just-in-Time) Compiler:
-
JavaScript Engine has the sole job to take JavaSctipt syntax in human readable form & converted into machine code (0 & 1s).
-
On the client side, it downloads the code, processes, and compiles.
-
That is why it is named as Just-in-Time JIT compiler.
JS Console
-
JavaScript console is an interface that allows a developer to input a command and view the output.
-
Every JS engine has its JS console.
-
It is like MS Command Line and Mac Terminal/
-
It is used for debugging & we can see what happens in JIT compiler.
-
To open the JS console in Develepor tool on browser follow the steps.
-
Open browser > Right click > Inspect > Console .

Right-click on blank page
Click on Inspect
-
Click on Console
-
& Write code here
Syntax & API
-
The syntax is the way of a program written.
-
Set of predefined functions by JIT compiler.
-
API: Application Program Interface. It is a set of own function() & properties . It has native API.
-
eg. JQuery, AnguarJS etc.
JQuery
-
It has own collections function() & properties defined by $.
-
Embedded API or extended AIP .
-
It needs JavaScript API to define its own API.
Primitive Datatypes
-
String: "Hello", 'Hello', "hello \"Dinesh\" ."...
-
Integer: 122, 12 ...
-
Floating: 1.2, 112.33 ...
-
Boolean: Stores true/false
-
Null: No value assigned.
-
undefined: void, empty.
-
NaN: Not a Number (If you store string in a number var).
Hello World
-
This is a basic a basic program of javascript written inside the HTML code.
-
We can put the the code where ever we want in html page.
-
There are 2 ways of putting javascript code.
-
Inside the <script> tag.
-
With the external .js file & give the link to the html page.
-
Here we have kept the the javascript code inside the <script> tag.
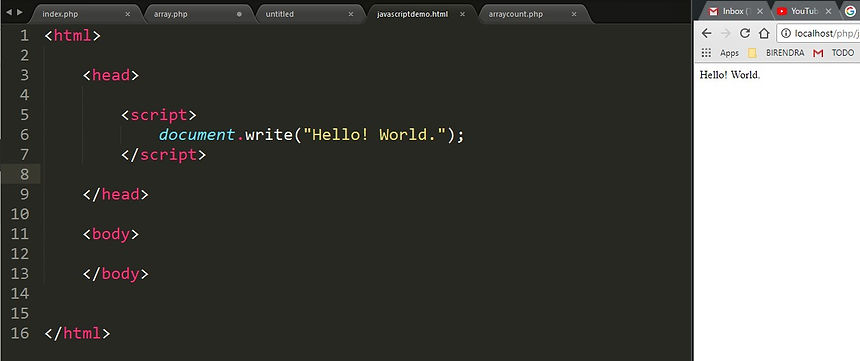
JavaScript code
Where to keep
-
There are 3 ways to keep the JavaScript code.
-
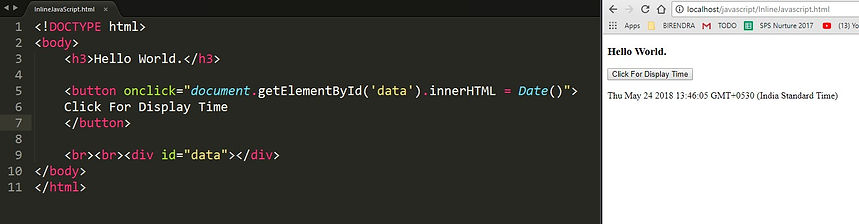
Inline JavaScript: To keep the JavaScript code in an attribute.
-
Internal JavaScript: To keep the JavaScript code in <script> tag in a HTML page.
-
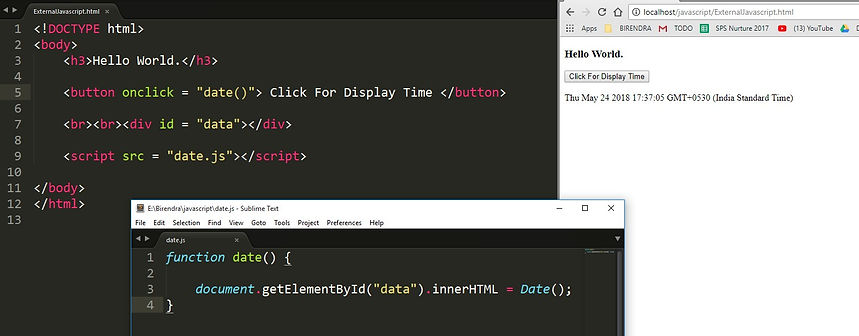
External JavaScript: To keep the javascript code in an external file (.js) and use that file on HTML page as a source.
1 Inline JavaScript
2 Internal JavaScript

3 External JavaScript
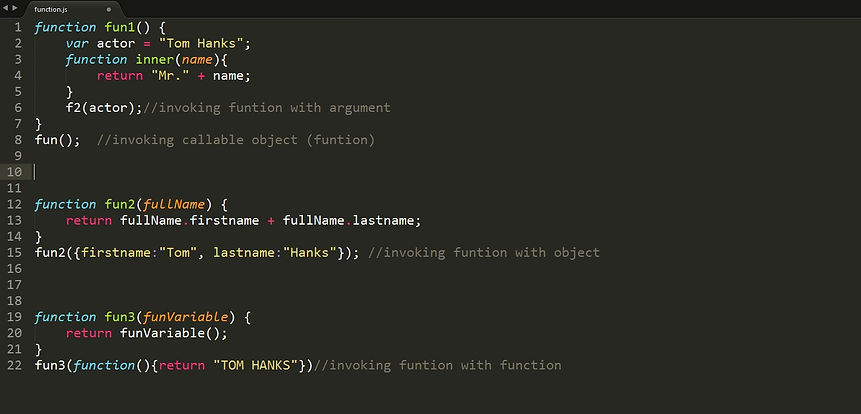
Function
-
A JavaScript function is a block of javascript code, that can be executed when called it .
-
A function can be called when an event occurs, like when the user clicks a button.
-
It is also known as a callable object.
-
All the variable declared inside a function is deleted after executed.
-
All function needs to invoked to be executed.
-
We can pass through a function:
-
Passing Argument.
-
Passing object.
-
Passing function.
Event
-
An HTML event can be something the browser does or something a user does.
-
JavaScript allows us to execute code when events are detected.
Display on HTML
-
There are different possibilities to display some string/data on HTML page using JavaScript.
-
Using innerHTML:
-
Here we can write an HTML element.
-
To access html element, JavaScript use document.getElementById (id) method.
-
innerHTML element property defines the HTML content, and we can assign any data.
-
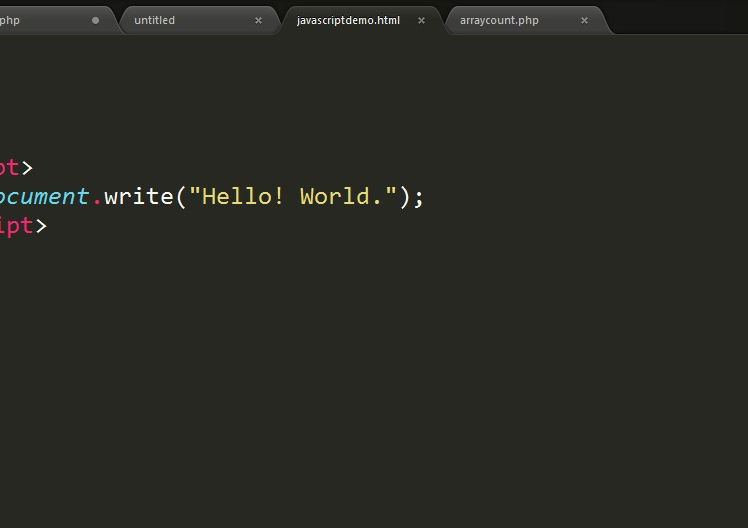
Using document.write():
-
We can use document.write(data) to write on the browser.
-
It will delete all the existing elements.
-
Using window.alert():
-
Here we can use the alert box to display the data.
-
Using console.log():
-
For debugging purpose, we can use console.log(data) method on browser's console.
JavaScript HTML DOM
-
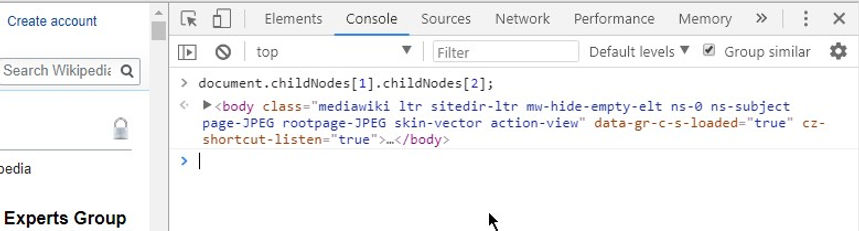
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
-
It simply representing all the HTML nodes or elements as objects in JavaScript.
-
The window object is used to represent the window to JavaScript, so we can get details & modify data.
-
So we can get details, modify the functionality and contents using JavaScript.
Document Object
-
The HTML DOM is constructed as a tree of objects.
-
Here is a picture represents the objects.
HTML DOM Tree of Objects
Document
Root Element:
<html>
Element:
<head>
Element:
<body>
Element:
<title>
Text:
"My text"
Attribute:
"href"
Element:
<a>
Text:
"My link"
Element:
<h1>
Text:
"My header"
-
With the object model, Javascript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic HTML.
-
In a page, JavaScript can:
-
change all the HTML elements, attributes, CSS styles.
-
add/remove existing elements and attributes.
-
react/create new HTML events.
HTML DOM Methods
-
HTML DOM methods are actions you perform & DOM properties are values that we can set on an HTML element.
-
This DOM can be accessed with JavaScript.
-
DOM document object is the owner of all other objects on our web page.
-
Below are some methods of the document to access & manipulate HTML.
-
For creating & deleting the HTML elements.
-
For changing the HTML existing elements.
-
You can add events of different types to the same element:
-
For creating an event in HTML.
bottom of page